Website owner: James Miller
INTEGRATION BY SUBSTITUTION
Integration by substitution. A very useful device for transforming a given integrand into a form in which the fundamental integration formulas can be applied is that of substituting a new variable. Consider the following example.
Example. Find
![]()
Solution. This integration cannot be performed directly by any of the standard formulas. Let us make the substitution
x = 2 sin θ
which will, we shall see, have the effect of transforming the integrand into a rational trigonometric function.
If x = 2 sin θ then dx = 2 cos θ dθ. We then have, upon substituting,
![]()
![]()
![]()
Now using the trigonometric identity cos 2θ = 2cos2 θ - 1 we get
![]()
= 2θ + sin 2θ + C .
We have thus performed the integration in terms of θ. We can now change the result back into terms of x as follows:
Since x = 2 sin θ,
![]()
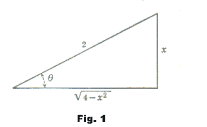
Using this relationship we construct the triangle shown in Fig. 1. We know two sides of the
triangle and get the other side from the Pythagorean theorem i.e. x2 + y2 = 22 so
![]() .
.
The trigonometric formula for sin 2θ is
sin 2θ = 2 sin θ cos θ .
Using Fig. 1 we have
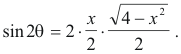
Thus
![]()
Trigonometric substitutions. Integrands of the following types are often encountered in applications:
![]()
where m is a positive or negative integer. Integrands which are algebraic and involve no irrational function of x aside from integral powers of one of the quantities
![]()
can be transformed into rational trigonometric functions by a trigonometric substitution of the following type:
![]()
![]()
![]()
It is easily seen that these substitutions convert the integrands to rational expressions in terms of trigonometric functions since
![]()
![]()
![]()
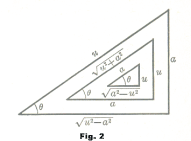
Appropriate triangle constructions such as those shown in Fig. 2 obviate the use of trigonometric identities in transforming integrands.
Integrands containing quantities of types
![]()
can be dealt with in a similar way. In this case make the substitutions as follows:
![]()
![]()
![]()
Miscellaneous substitutions.
I If an integrand is rational except for a radical of the form
![]()
it can be rationalized by a substitution as follows:
![]()
![]()
![]()
substitute q + px - x2 = (α + x)2z2 or q + px - x2 = (β - x)2z2
II Any rational function of sin θ and cos θ can be replaced with a rational function of z by using the substitution
θ = 2 tan-1 z
since
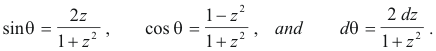
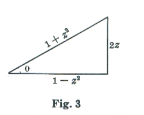
The first and second of these relationships are obtained from Fig. 3 and the third by differentiating
θ = 2 tan-1 z .
The relationships shown in Fig. 3 are obtained from the trigonometric double-angle formula
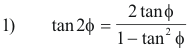
which is equivalent to
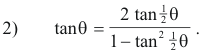
Since θ = 2 tan-1 z ,
![]()
and substituting into 2) we obtain
![]()
from which we construct the triangle of Fig. 3.
III Theorem. If in
![]()
m, n, p, q are integers, the substitution
![]()
will rationalize
![]()
provided that
![]()
is a positive or negative integer or zero.
Evaluating integrals of types:
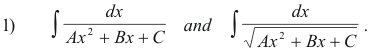
By using the process of “completing the square”, one can write any quadratic function Ax2 + Bx + C in one of the forms (u2 + a2), (u2 - a2), (a2 - u2), (-a2 - u2), possibly multiplied by a constant, where u is some linear function of x. The integrals 1) are thus turned into standard forms.
Reduction of Ax2 + Bx + C to one of the forms (u2 + a2), (u2 - a2), (a2 - u2) or (-a2 - u2). The function Ax2 + Bx + C can be written as
![]()
where p =B/A and q = C/A. Now we complete the square on x2 + px + q:
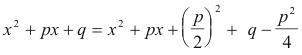
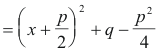
Thus we have
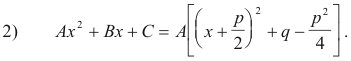
Set
![]()
and
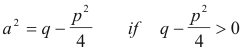
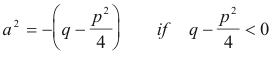
From 2) we see that the function Ax2 + Bx + C can now be written as one of the forms (u2 + a2), (u2 - a2), (a2 - u2) or (-a2 - u2), depending on the sign of A (with the sign of A transferring).
Other substitutions.
1. The substitution ex = z reduces
![]()
2. The substitution tan x/2 = z reduces
![]()
3. The substitution x = 1/z reduces
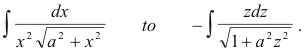
Change of limits corresponding to a change of variable. When one does a change of variable in a definite integral he can avoid the trouble of changing the result back into terms of the original variable by making a corresponding change in the limits as illustrated in the following example.
Example. Evaluate
![]()
Solution. Let us use the substitution x = 4 sin θ. The integration is over the x-interval from x = 0 to x = 4. The corresponding interval for the new variable is found from the relation x = 4 sin θ as follows:
Putting x = 4:
4 = 4 sin θ, sin θ = 1, θ = π/2
Putting x = 0:
0 = 4 sin θ, sin θ = 0, θ = 0
The θ interval that corresponds to x = 0 to x = 4 is then θ = 0 to θ = π/2. Hence,
![]()
Substitutions in general. A considerable amount of ingenuity is required choosing a substitution that will simplify a given integral. We have covered some of the most useful transformations. However we have by no means exhausted the possibilities. One is free at any time to make any change of variable that he pleases. If the integration can be performed in terms of the new variable, the result can easily be changed back into terms of the original variable.
Important transformations. The following list gives some transformations and their effects.
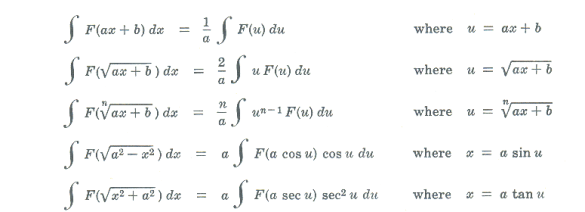
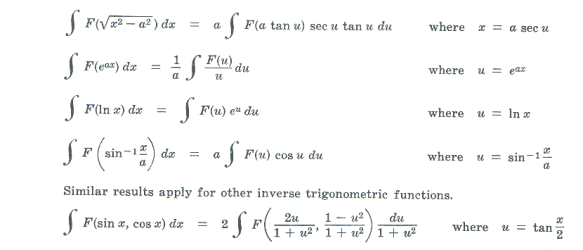
Jesus Christ and His Teachings
Way of enlightenment, wisdom, and understanding
America, a corrupt, depraved, shameless country
On integrity and the lack of it
The test of a person's Christianity is what he is
Ninety five percent of the problems that most people have come from personal foolishness
Liberalism, socialism and the modern welfare state
The desire to harm, a motivation for conduct
On Self-sufficient Country Living, Homesteading
Topically Arranged Proverbs, Precepts, Quotations. Common Sayings. Poor Richard's Almanac.
Theory on the Formation of Character
People are like radio tuners --- they pick out and listen to one wavelength and ignore the rest
Cause of Character Traits --- According to Aristotle
We are what we eat --- living under the discipline of a diet
Avoiding problems and trouble in life
Role of habit in formation of character
Personal attributes of the true Christian
What determines a person's character?
Love of God and love of virtue are closely united
Intellectual disparities among people and the power in good habits
Tools of Satan. Tactics and Tricks used by the Devil.
The Natural Way -- The Unnatural Way
Wisdom, Reason and Virtue are closely related
Knowledge is one thing, wisdom is another
My views on Christianity in America
The most important thing in life is understanding
We are all examples --- for good or for bad
Television --- spiritual poison
The Prime Mover that decides "What We Are"
Where do our outlooks, attitudes and values come from?
Sin is serious business. The punishment for it is real. Hell is real.
Self-imposed discipline and regimentation
Achieving happiness in life --- a matter of the right strategies
Self-control, self-restraint, self-discipline basic to so much in life