Website owner: James Miller
POLAR COORDINATES

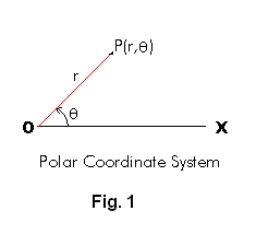
Polar Coordinate System. A coordinate system in which the position of a point P(r, θ) is given by its radial distance r from an origin O and the angle θ measured counterclockwise from a horizontal line OX called the polar axis to line OP. See Fig. 1. The line OP from the origin to the point is called the radius vector, the angle θ is called the polar angle, and the origin O is called the pole.
Transformations between polar and rectangular coordinates. The formulas for converting from rectangular to polar coordinates or vice versa are:
x = r cos θ
y = r sin θ
θ = arc tan y/x
![]()
Slope in polar coordinates. Whereas in rectangular coordinates dy/dx represents the slope of the curve y = f(x), in polar coordinates dr/dθ does not represent the slope of the curve r = f(θ). It merely represents the rate of change of the radius vector r with respect to the angle θ. In order to determine the slope in polar coordinates we use the relations
x = r cos θ
y = r sin θ .
Thus
![]()
![]()
and
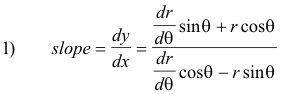
Angle ψ from the radius vector to the tangent. The angle ψ from the radius vector to the tangent (measured counterclockwise) is an important angle that plays a role in polar coordinates somewhat similar to that of the slope in rectangular coordinates. It is given by
![]()
where r' = dr/dθ. See Fig. 2.
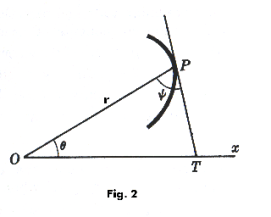
Angle of intersection between two curves. The angle of intersection f12 between two curves C1 and C2 meeting at a point P, not the pole, is given by
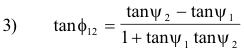
where ψ1 and ψ2 are the angles from the radius vector OP to the respective tangents to the curves at P and f12 is the angle measured counterclockwise from the tangent of curve C1 to the tangent of curve C2. See Fig. 3.
Differential of arc length. The differential of arc length is given by
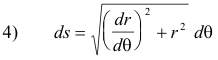
which can also be written as
![]()
Curvature. The curvature of a curve at a point P is given by
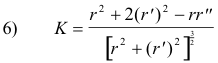
where r' = dr/dθ.
Finding points of intersection. The points of intersection of two curves whose equations are
r = f1(θ)
r = f2(θ)
can often be found by solving
7) f1(θ) = f2(θ)
Example. Find the points of intersection of r = 1 + sin θ and r = 5 - 3 sin θ.
Solution. Set 1 + sin θ = 5 - 3 sin θ. We get sin θ = 1. Thus θ = π/2 and (2, π/2) is the only point of intersection.
When a pole is a point of intersection, it may not appear among the solutions of 7).
Jesus Christ and His Teachings
Way of enlightenment, wisdom, and understanding
America, a corrupt, depraved, shameless country
On integrity and the lack of it
The test of a person's Christianity is what he is
Ninety five percent of the problems that most people have come from personal foolishness
Liberalism, socialism and the modern welfare state
The desire to harm, a motivation for conduct
On Self-sufficient Country Living, Homesteading
Topically Arranged Proverbs, Precepts, Quotations. Common Sayings. Poor Richard's Almanac.
Theory on the Formation of Character
People are like radio tuners --- they pick out and listen to one wavelength and ignore the rest
Cause of Character Traits --- According to Aristotle
We are what we eat --- living under the discipline of a diet
Avoiding problems and trouble in life
Role of habit in formation of character
Personal attributes of the true Christian
What determines a person's character?
Love of God and love of virtue are closely united
Intellectual disparities among people and the power in good habits
Tools of Satan. Tactics and Tricks used by the Devil.
The Natural Way -- The Unnatural Way
Wisdom, Reason and Virtue are closely related
Knowledge is one thing, wisdom is another
My views on Christianity in America
The most important thing in life is understanding
We are all examples --- for good or for bad
Television --- spiritual poison
The Prime Mover that decides "What We Are"
Where do our outlooks, attitudes and values come from?
Sin is serious business. The punishment for it is real. Hell is real.
Self-imposed discipline and regimentation
Achieving happiness in life --- a matter of the right strategies
Self-control, self-restraint, self-discipline basic to so much in life